The stock market is not only a way to make money but also a path to financial literacy and participation in the development of the modern world.
The essence of the stock market
The stock market is an organized system for trading securities such as stocks, bonds, investment funds and other financial instruments. Its main function is to provide companies with the opportunity to raise funds for development and to offer investors a platform for placing their capital to generate income.
In other words, the stock market is where supply and demand for capital meet. Companies offer their securities (supply), and investors buy them (demand). For companies, this is an effective way to finance themselves without having to take out bank loans, and for investors, it is a chance to become co-owners of companies and profit from their success.
Main types of securities
There are many financial instruments traded on the stock market, but the most common are stocks and bonds.
Stocks
A stock is a document that confirms ownership of a share in a company. By purchasing stocks, an investor becomes a co-owner of the company, can receive dividends (a portion of the profits), and earn money on the market growth.
For example, if you bought Apple shares for $150 and a year later their price rose to $180, the difference of $30 is your profit. In addition, the company may pay dividends.
Bonds
A bond is a debt security. When you buy one, you are lending money to the issuer ( a company or government) at a fixed interest rate for a specific term. At the end of the term, you get your principal back and receive interest payments.
Bonds are often considered a more stable investment option because they carry less risk than stocks.
Other instruments
The market also offers:
investment funds (ETFs, mutual funds);
derivatives (futures, options);
depositary receipts (ADRs), which allow you to invest in foreign companies
How the stock market works
The stock market operates through stock exchanges - special organizations that create conditions for trading securities
Exchanges and their role
The world’s most famous exchanges:
New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) - the largest in the world. Shares of companies such as Coca-Cola, Visa, IBM, and Procter&Gamble are traded here.
NASDAQ - an electronic exchange known for its technology giants: Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Google, and Tesla.
London Stock Exchange (LSE) - one of the oldest, important for the European financial market.
Exchanges do not buy shares directly, but act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, ensuring transparency and security of transactions.
The role of brokers
Most investors conduct transactions through brokers - licensed intermediaries who have access to exchanges.
How companies go public
When a company decides to sell its shares publicly for the first time, it is called an IPO (Initial Public Offering) or SPAC. During an IPO, the company receives funds from investors, and they receive a share in the company’s ownership.
For example, during its IPO in 2012, Facebook (Meta) raised over $16 billion, which allowed it to expand its operations and finance new projects.
After an IPO, the company’s shares are freely traded on the stock exchange - investors can buy and sell them at any time.
How the share price is formed
The share price is determined by supply and demand. If more investors want to buy a share than sell it, the price rises. If the opposite is true, it falls.
Factors influencing price changes:
the company’s financial performance;
the state of the economy;
political events;
industry news;
investor sentiment;
For example, a positive report from Apple on sales growth often increases demand for its shares and, consequently, their price. Conversely, news of production disruptions can lead to a fall in market capitalization.
Who participates in the stock market
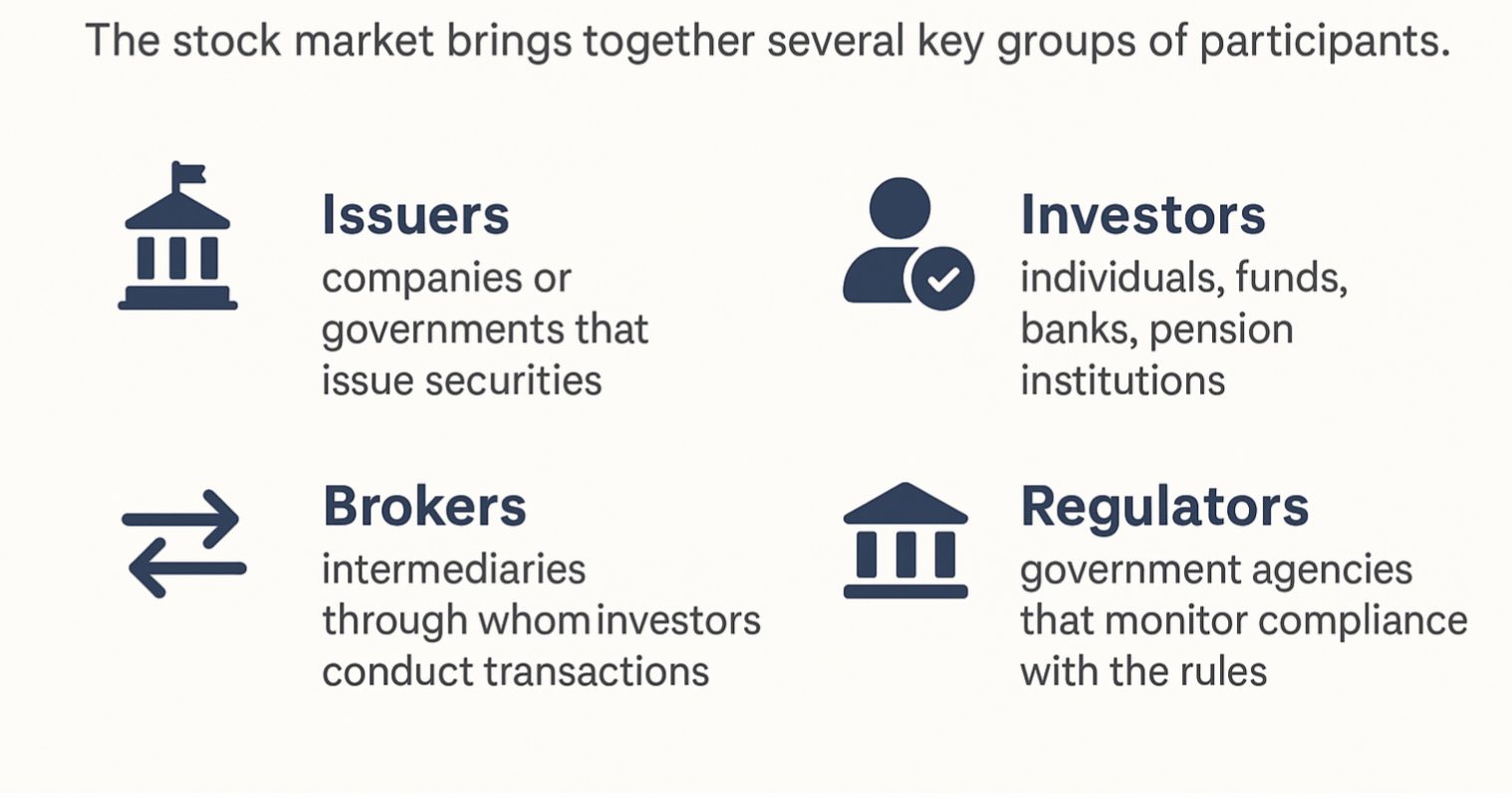
In the USA, the main regulator is the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission). It ensures market transparency, prevents fraud, and protects investors.
The role of the stock market in the economy
The stock market is a key mechanism for economic development. Its main functions are:
Raising capital: companies obtain financial resources for development.
Redistribution of resources: money flows from savers to businesses that create value.
Valuation: The market determines the fair price of a company through supply and demand.
Supporting liquidity: investors can quickly sell their assets if necessary.
Stimulating growth: business development contributes to job creation and increased prosperity.
Main risks of investing
Investing in the stock market always involves certain risks. The most common ones are:
Market risk — changes in the economic situation can affect stock prices.
Credit risk — the bond issuer may not repay the debt.
Currency risk — currency fluctuations affect international investments.
Inflation risk — rising prices can reduce real returns.
To reduce risks, investors use diversification — spreading their funds across different types of assets, companies and industries.
Examples from the US stock market
The American stock market is the largest and most influential in the world. Its experience often is a model for other countries.
New York Stock Exchange
Founded in 1792, the NYSE is a symbol of global finance. Today, more than 2,400 companies are traded here, with a total market capitalisation of over $30 trillion.
The example of Apple
Apple Inc. first went public in 1980. At that time, the price of one share was $22. Today, Apple is one of the most valuable companies in the world, with a market value of almost $4 trillion. For investors who invested in Apple early on, it was one of the most successful decisions in history.
NASDAQ and tech giants
The NASDAQ stock exchange has become a hub for the development of tech companies such as Amazon, Microsoft, Google, Tesla, and Netflix. The high volatility of these stocks makes them attractive to active investors, although the risk is also greater.

How to Start Investing
Starting your investment journey may seem intimidating at first, but with the right mindset and a few practical steps, it becomes a rewarding and empowering process. Here’s how to begin:
1. Define your goals
Before you invest a single dollar, understand why you’re doing it. Are you saving for retirement, building an emergency fund, planning for a child’s education, or simply looking to grow your wealth? Clear goals help determine your strategy, time horizon, and level of acceptable risk.
2. Choose a reliable platform
Select a trusted investment partner like Fondexx, known for its transparency, user-friendly tools, and strong reputation. A good platform provides not only access to markets but also education and guidance to help you make informed decisions.
3. Learn the basics
Familiarize yourself with the fundamentals of investing: how the stock market works, what stocks, bonds, ETFs, and mutual funds are, and how risk and return are connected. The more you understand, the more confidently you’ll manage your money.
4. Start small — and stay consistent
You don’t need a large amount of money to begin. Even small, regular investments can grow significantly over time through the power of compounding. Start with what you’re comfortable with and increase your contributions as you gain experience.
5. Diversify your portfolio
Avoid putting all your money into one company or asset type. Spread your investments across different sectors and regions. Diversification helps reduce risk and makes your portfolio more resilient to market fluctuations.
6. Keep emotions out of your decisions
Markets can be unpredictable, and it’s easy to get caught up in fear or excitement. Instead, stick to your plan, review your progress periodically, and make adjustments based on logic — not emotion.
7. Keep learning and adapting
Investment is a continuous learning process. Stay informed about economic trends, company performance, and global events that may affect your portfolio. Over time, you’ll refine your strategy and become more confident in your choices.
Conclusion
The stock market is an integral part of the global economy. It helps companies raise capital, investors grow their savings, and countries stimulate economic growth.
Its operation is based on trust, transparency, and a balance of interests among all participants. Those who understand its principles gain not only financial benefits but also a deeper understanding of how the global economy works.